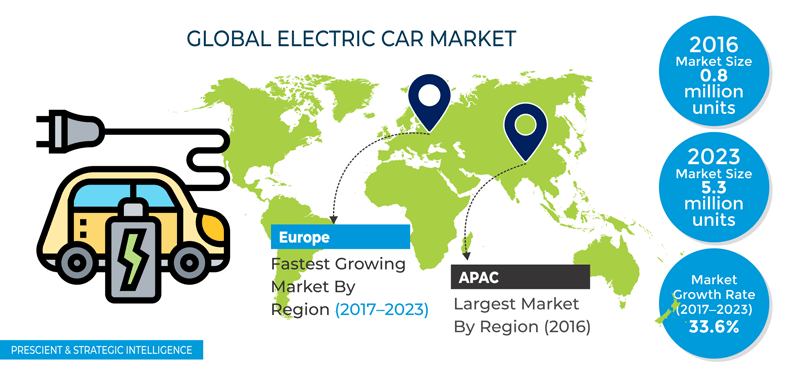
The Global Electric Vehicle Market size is expected to rise from 4,093k units in 2021 to 34,756k units by 2030 .i.e. a growth of 27%. The factors such as low emission transportation or government support to EV projects, subsidies & tax discounts for the zero-emission vehicle industry have supported the manufacturers immensely to produce large-scale electric vehicles. This has generated huge demand for electric vehicles in the market worldwide. The countries around the world have already set their respective targets for emission reductions concerning their desired capacity. Recent research reveals that the electric vehicle market worth is expected to reach around $ 802.81 billion by 2027 with a 41 % rate of growth 2020-27. Then, what is mean by electric vehicle?
What is Electric Vehicle (EV)?
EVs or electric vehicles are vehicles that are semi or fully powered by electricity. Electric vehicles have relatively cheaper running costs because they have a lesser number of moving parts for maintenance. Most importantly, they are eco-friendly as there is hardly any use of fossil fuels (petrol or diesel). In economics, an electric vehicle (EV) means the vehicle that operates via an electric motor instead of an internal combustion engine.
Though there is the use of lead-acid or nickel-metal hydride batteries in some EVs, lithium-ion batteries are used in most EVs. These lithium-ion batteries are durable and have an excellent capacity for retaining energy. It has a very low self-discharge rate per month that is nearly 5%. Despite the advantages of lithium-ion batteries, there are large-scale challenges for these batteries for experiencing thermal runaway. Greater efforts are being made to improve the safety of these batteries as they are vulnerable to fire and explosions.
Basic principles of working an Electric Vehicle
The electric vehicle works on the basic principle-conversion of energy. In EVs, the electric energy gets converted into mechanical energy. The use of a motor in the electrical system is done for conversion. The motor plays the same role in an electric vehicle as what an internal combustion engine plays in an IC vehicle.
In electric vehicles, electricity moves from the battery to the controller. Then, the controller supplies electricity to electric motors as and when required. The accelerator connects to a variable switch that controls how much power to be supplied to the electric motors. Power output varies from zero to full as required. Electric vehicles have following types of on-board energy storage systems:
- Electrochemical energy
- Static energy
- Kinetic energy
Types of electric vehicles (EVs)
- Battery Electric Vehicles (BEV)
- Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEV)
Battery Electric Vehicles (BEV): If you compare these vehicles with an internal combustion engine, BEVs have 99% lesser moving parts for maintenance. You can charge BEVs at home overnight so that you will have the luxury of getting enough power for traveling. The typical charging of an electric vehicle runs from 30 minutes to even more than 12 hours. Of course, this depends on the speed of the charging station and battery capacity. The advantages of BEV include:
- Lesser noise level
- No exhaust, clutch or gears and spark plugs
- No use of fossil fuels rather rechargeable batteries
Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEV): Here, it doesn’t depend completely on an electric motor. In hybrid electric vehicles, you will find a combination of battery and fossil fuel (Petrol & Diesel) power. This helps the user to travel long distances as the person can switch to traditional fuel whenever there is a need instead of solely depending on the chargeable battery. But it needs more maintenance, a noisy engine, high emission, and high fuel cost. PHEVs have smaller battery packs with a reduced range.