Electric Vehicle is a form of transport that employs electric power in place of gasoline or fossil fuel. To provide energy to the electric vehicle motors batteries are required. Electric vehicle incorporates one or more than one electric motors to create motion. In spite of differences in engines, the electric vehicles are more or less similar to traditional cars. Their internal and external view is same. External design is almost similar due to modern style and aerodynamic properties.
When we think of electric vehicles that means we think of electric cars. In simpler terms, an electric vehicle is that operates via an electric motor instead of an Internal Combustion Machine. Such technology is not only used in electric cars but also in trucks, trains, boats, planes and bikes.
How do electric vehicles work?
Electric vehicles are similar to automatic cars. These vehicles work in both forward and reverse mode. When the rider puts the vehicle in gear and press the accelerator pedal, the following things happen:
Step 1: The power gets converted from DC battery to AC in the electric motor.
Step 2: The accelerator pedal gives signal to the controller. It adjusts the vehicle’s speed by changing the frequency of AC power from the inverter to motor.
Step 3: The motor connects and starts turning the wheels via a cog.
Step 4: When the brakes are applied on the vehicle or the car is retarded, the motor turns into an alternator and starts producing power that is in turn sent back to the battery.
AC or DC Electric Cars
AC or Alternating current changes direction at a definite frequency that is just like the pendulum of a clock. DC or Direct Current travels in one direction only that is positive to negative.
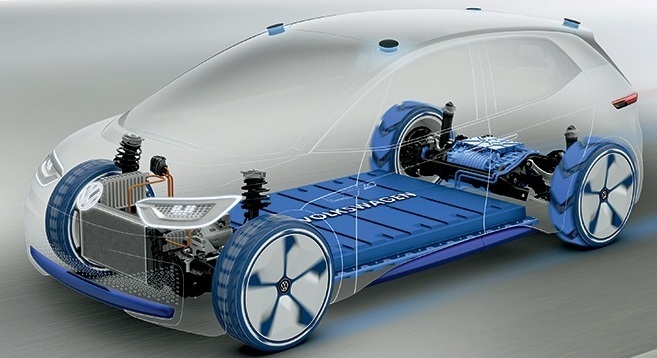
Main Components of Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs)
- Electric Motor: There is a presence of electric motors in majority of electrical appliances starting from grinders, washing machines, dryers to robots. The electric motors are highly popular, durable and trustworthy. It uses AC power.
- Battery: The electric vehicle has a battery that stores electrical energy. The battery pack is composed of several cells that are combined to form modules. If there is enough energy in the battery, the vehicle would be ready to be used. These EV batteries are lithium-based and having a very low volume of discharge. That means once it is charged, it holds the charge for few days or weeks.
- Inverter: The inverter converts DC to AC power in the electric motor. The inverter changes the speed in which the motor revolves by adjusting the frequency of alternate current. It also increases or decreases the power of the motor with the amplitude of the signal.
- Battery Charger: The battery charger alters the electric power available from the sources to DC stored in the battery. It regulates the voltage level of the cells by controlling the rate of charge.
- Controller: The controller is regarded as the brain of the vehicle that regulates all its parameters. It changes the rate of charge from the information received from the battery. It also uses the pressure on the accelerator pedal for adjusting the speed of the motor inverter.
- Charging Cable: The charging cable for simple charging connects the battery to the power source points.
Electric vehicles have been emerged as the future of transport. There is a large-scale support to the use of electric vehicles because of its econ-friendly nature and low carbon emissions. Then, it is more economical compared to traditional vehicles using fossil fuels. These electric vehicles are much cheaper to manufacture than the conventional vehicles.